
This procedural lab is a great compliment for genetic studies where students learn about sex linked genes and mutations. The allele for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy is located on the X chromosome and is associated with a deletion mutation for that region.
This defective section of DNA is shorter than the wild-type (normal) allele. When run through gel, the shorter, mutant fragments will move farther. Students can directly observe this. Hint: have students place the gel chambers on white paper for a better view.
Students use dyes to simulate DNA samples from a family where the mother is a known carrier. Students will also learn how to set up electrophoresis chambers. They load the wells with a micropipet and observe how the dye moves through the gel. Finally, they analyze the banding pattern to determine is the section is short (mutant) or normal length.
Biotechnology in the Lab
Students get the experience of gel electrophoresis, but the focus of the exercise is on NGSS standard regarding the relationship between genes, chromosomes, and traits.
Background knowledge regarding Mendelian genetics and sex-linked crosses is helpful, but not necessary if you wanted to use this exercise to introduce the topics.
The equipment is expensive, and for many years I borrowed the chambers from a nearby university. You can order the electrophoresis chambers and power supplies from biological supply companies and from Amazon.
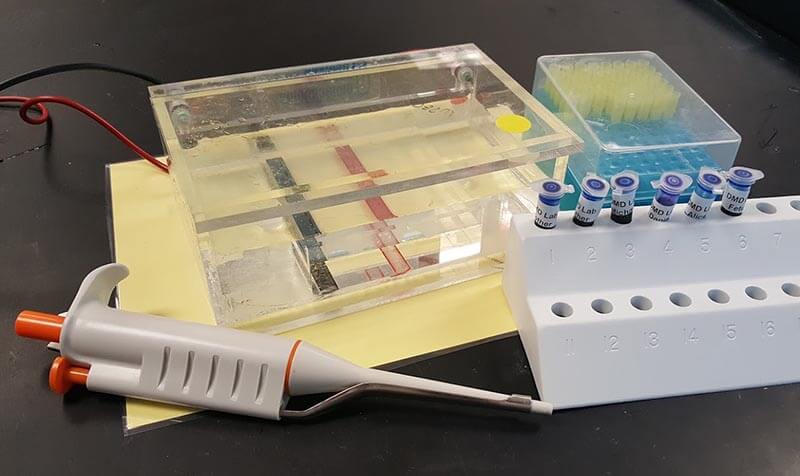
The dye samples can also be ordered from supply companies, instructions on making the dye is included, but I believe you can purchase dye sets that are pre-made.
If you do not have access to the equipment, you can use the Penguins and DNA sequencing which models the techniques on paper. In this exercise, students use sequencing to identify species of penguins.
Grade Level: 11-12
Time Required: 2 class periods, 1 to discuss scenario and create gels, 2nd day for running samples and analysis
HS-LS3-1 Ask questions to clarify relationships about the role of DNA and chromosomes in coding the instructions for characteristic traits passed from parents to offspring.
CCC 1. Patterns. Observed patterns of forms and events guide organization and classification, and they prompt questions about relationships and the factors that influence them.

