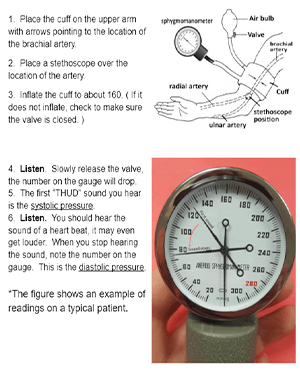
Students are familiar with getting their blood pressure taken at a doctor’s office, but many do not know how the device works. A sphygmomanometer is a device that can be used to measure blood pressure. Students learn to measure their blood pressure in this activity.
The device works with a cuff that is inflated to temporarily restrict blood flow. You place a stethoscope just under the cuff where you can listen to the sounds of blood in the brachial artery. When the valve is released, the needle will drop.
The first sound you hear with the stethoscope is the systolic pressure, in typical readings, this will occur between 110 and 140. Continue to listen until you no longer hear the thumping sound (it will sound like a heartbeat). The point at which you no longer hear the sound is the diastolic pressure, which typically occurs around 60-70. The blood pressure is read as two numbers. A typical blood pressure reading is 120/70.
Measuring blood pressure takes practice! I tell my class that nursing students may take days to really master the procedure. Since we only have a class period to practice, some students will struggle. I usually have digital blood pressure devices for students to use and compare their manual readings.
Blood pressure cuffs are fairly inexpensive, I usually have about 12 for the class. I have a 4 digital wrist monitors, though I have found the readings on the wrist monitors are not always accurate.
If you are purchasing a cuff, make sure you get a kit that also includes a stethoscope. Stethoscopes can also be used to measure heart sounds.
The lab handout includes a section with instructions, but I usually just put the instructions on the overhead and do a demonstration. (The last page of the download has large print instructions for display.) Then let students try it for themselves. Amazingly, kids stay busy and engaged in this lab. They love playing with medical toys. I even have a few finger pulse monitors for them to use. I include this activity as part of a larger unit on the circulatory system which also includes a sheep heart dissection.

