Sheep Heart Dissection - A Step by Step Guide
Materials
External Anatomy
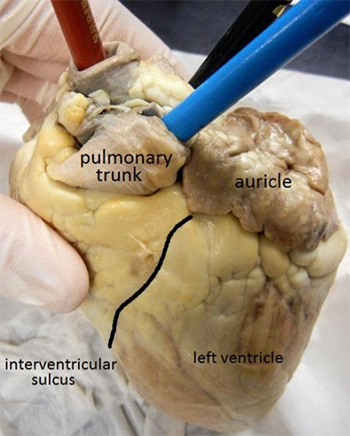
1. Identify the right and left sides of the heart. Look closely and on one side you will see a diagonal line of blood vessels that divide the heart, this line is called the interventricular sulcus.
2. The half that includes the apex (pointed end) of the heart is the left side. The flaps that cover the atria are called auricles. Locate the apex and the auricles. ![]()
3. Locate the coronary arteries and veins that are on the surface of the heart. ![]()
4. Find the flaps of dark tissue on the top of the heart. These ear-like flaps are called auricles. ![]()
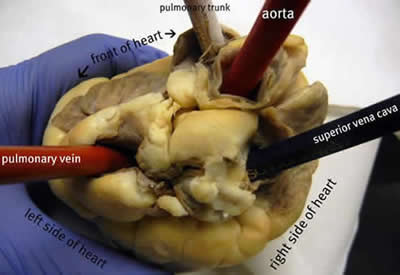
5. Tne front-most vessel is the pulmonary trunk. Place a probe or pencil in this vessel to mark its place. ![]()
6. Just behind the pulmonary trunk is the aorta. Depending on how the heart was removed, you might also see a branch of the aorta called the brachiocephalic artery. Place a pencil or probe in the aorta to mark its place. ![]()
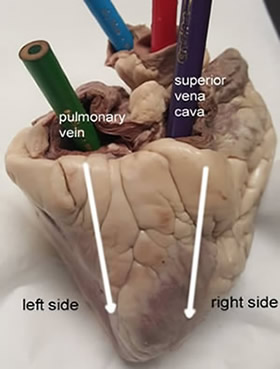
6. Turn the heart so that you are looking at its dorsal side (the back of the heart.) Find the large opening at the top of the heart next to the right auricle. This is the superior vena cava. Place a pencil in this vessel, you may also use your finger to feel the inside of the right atrium. ![]()
7. Compare the thickness of the pulmonary trunk to the aorta. Try placing your finger in each, make a note of
the resistance and thickness of the two vessels. Explain WHY they are different.
8. Turn the heart so that you are looking at its dorsal side (the back of the heart.) Find the large opening at
the top of the heart next to the right auricle. This is the superior vena cava. Place a pencil in this vessel, you may also use your finger to feel the inside of the right atrium. ![]()
9. Locate another opening on the backside of the heart on the left side. This is the pulmonary vein. You can feel the inside of the right atrium by probing this opening with your finger. Place a pencil in the pulmonary vein opening. ![]()
10. Checkpoint: Make sure you know the location of each of the following before continuing to the internal anatomy of the heart:
superior vena cava
inferior vena cava
aorta
pulmonary arterypulmonary veins
left atrium & ventricleright atrium and ventricle
auricleapex
coronary arteries & veins
interventricular sulcus
11. Place pins or colored pencils in each of the main vessels that attach to the heart. Upload the photo with labels to Google Classroom.
12. Visually (or use diagrams) to indicated which vessels connect to which chambers:
Pulmonary artery to the ____________________
Pulmonary vein to the _____________________
Aorta to the _____________________________
Superior vena cava to the __________________
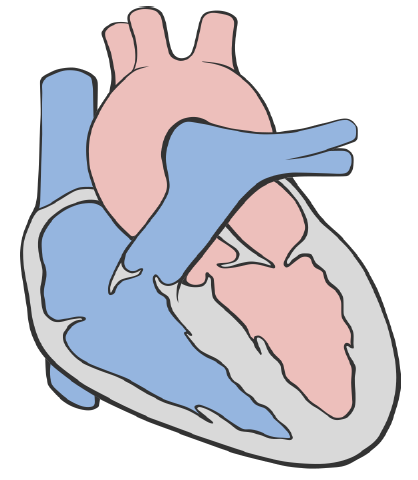
13. Label the vessels and chambers on the diagram. (You can abbreviate.)
Dissection: Internal Anatomy
14. Use a scalpel to make an incision in the heart just behind the aorta. Cut the heart in half so that the front of the heart separates from the back of the heart .
15. Locate the right atrium, the right ventricle, and the tricuspid valve between them. ![]()
16. The chordae tendineae, also called the "heartstrings" can be found attached to the thin flaps of the tricuspid.
They are anchored to the wall of the heart at the papillary muscle. ![]()
17. Locate the left atrium, left ventricle, and the bicuspid (mitral) valve. Note that the left side of the heart has a much thicker muscular wall. ![]()
18. Locate the chordae tendineae and the papillary muscle. ![]()
19. Insert a probe into the aorta and observe where the probe exits the heart. You may even be able to find the small aortic semilunar valve at the place where the aorta connects to the heart.
To what chamber does the probe connect? ____________________
20. Place a probe in the pulmonary artery.
To what chamber does the probe connect? ______________________________________________
What is the name of the valve in this artery? _____________________________________________
21. The heart has three layers: the epicardium, endocardium, and myocardium. Describe each layer from your
specimen. You may need to refer to your notes.
** Compare the heart of the sheep to human hearts by viewing various heart models in the room. 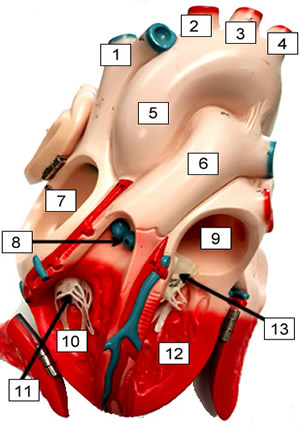
Label the Heart
1. ______________________
2. ______________________
3. ______________________
4. ______________________
5. ______________________
6. ______________________
7. ______________________
8. ______________________
9. ______________________
10. _____________________
11. _____________________
12. _____________________
13. _____________________
14. What muscles attach to the chordae tendinae to hold the valves in place? _____________________________
15. What are the flaps on the front of the atria called? __________________________
16. If you place a probe in the aorta, into what chamber will it exit? __________________________
17. The superior and inferior vena cava enter into what chamber of the heart? __________________________
18. The large vessel on the front of the heart that lies in front of the aorta is the __________________________
19. What are the tendons that connect the valves to the muscles ? __________________________
20. What is another name for the bicuspid valve? __________________________
21. Complete the drawing of the heart shown in the outline below. Label at least five structures.