Rat Dissection - The Urogenital System
Excretory Organs
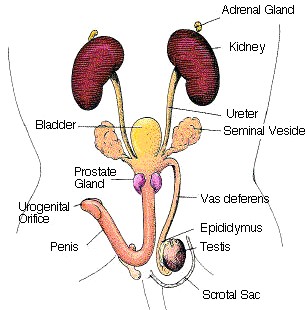
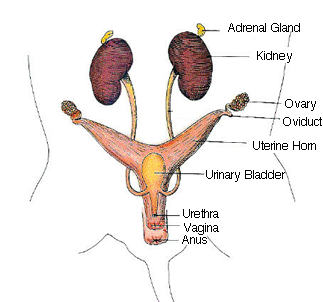
1. The primary organs of the excretory system are the kidneys. These organs are large bean shaped structures located toward the back of the abdominal cavity on either side of the spine. Renal arteries and veins supply the kidneys with blood.
Healthy kidneys filter about a half cup of blood every minute, removing wastes and extra water to make urine. The urine flows from the kidneys to the bladder through two thin tubes of muscle called ureters, one on each side of your bladder.
2. Locate the delicate ureters that attach to the kidney and lead to the bladder. Wiggle the kidneys to help locate these tiny tubes.
Ureters drain fluid from the kidneys and store it in the urinary bladder.
3. The urethra carries urine from the bladder to the urethral orifice (this orifice is found in different areas depending on whether you have a male or female rat).
4. The small yellowish glands embedded in the fat atop the kidneys are the adrenal glands.
The Reproductive Organs of the Male Rat
1. The major reproductive organs of the male rat are the testes (singular: testis) which are located in the scrotal sac. Cut through the sac carefully to reveal the testis. On the surface of the testis is a coiled tube called the epididymus, which collects and stores sperm. The tubular vas deferens moves sperm to the urethra, which carries it though the penis and out the body.
2. The lumpy brown glands located to the left and right of the urinary bladder is the seminal vesicles. The gland below the bladder is the prostate gland and it is partially wrapped around the penis. The seminal vesicles and the prostate gland secrete materials that form the seminal fluid (semen). Procedure: Pin the organs of the urogenital system.
The Reproductive Organs of the Female Rat
1. The short gray tube lying dorsal to the urinary bladder is the vagina. The vagina divides into two uterine horns that extend toward the kidneys. This duplex uterus is common in some animals and will accommodate multiple embryos (a litter). In contrast, a simple uterus, like the kind found in humans has a single chamber for the development of a single embryo.
2. At the tips of the uterine horns are small lumpy glands called ovaries, which are connected to the uterine horns via oviducts
Rat Navigation
Step 1: Body Regions
Step 2: External Features
Step 3: Expose the Muscles
Step 4: Expose the Bones
Step 5: Head & Neck
Step 6: Thoracic & Abdomen
Step 7: Urogenital System