Biotechnology
- Cloning
- Recombinant DNA Technology
- Gene Sequencing (Human Genome Project)
- Gene Therapy
- DNA Fingerprinting (and other Forensics applications)
- CRISPR-Cas9
DNA Cloning
Cloning is the production of identical copies of DNA
- Stems or root send up new shoots that are clones of the parent plant.
- Members of a bacterial colony on a petri dish are clones because they all came from division of the same cell.
- Human identical twins are clones; the original single embryo separate to become two individuals. (Artificial Twinning)
- Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer (SCNT) – adult cells used to create an embryo
Gene cloning is production of many identical copies of the same gene.
- If the inserted gene is replicated and expressed, we can recover the cloned gene or protein product.
- Cloned genes have many research purposes: determining the base sequence between normal and mutated genes, altering the phenotype, obtaining the protein coded by a specific gene, etc.
- Humans can be treated with gene therapy: alteration of the phenotype in a beneficial way.
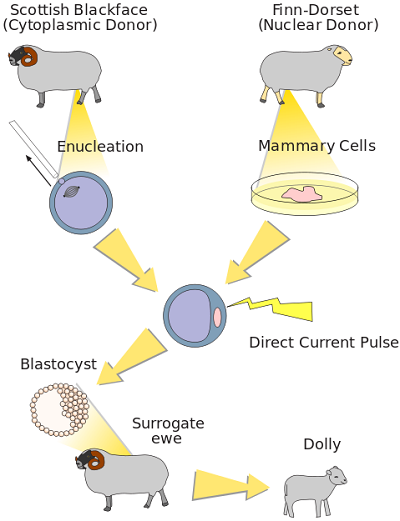
Cloning Animals
1. The cloning of Dolly in 1997 showed that mammals could be cloned.
2. Cloning of mammals involves injecting the nucleus of an adult cell into an enucleated egg.
3. The cloned eggs begin development in vitro and are then returned to host mothers until the clones are born.
Recombinant DNA Technology
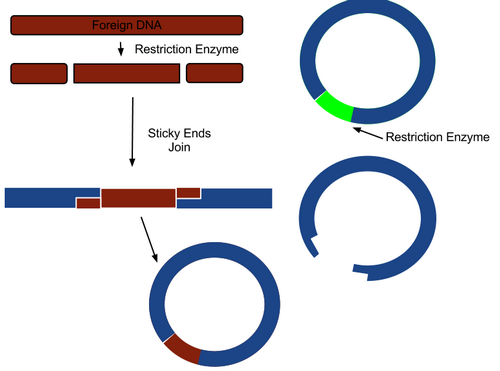
- Recombinant DNA (rDNA) contains DNA from two or more different sources.
- A vector is a plasmid or a virus used to transfer foreign genetic material into a cell.
- A plasmid is a small ring of DNA in the cytoplasm of some bacteria.
- Introduction of foreign DNA into vector DNA to produce rDNA requires two enzymes.
- Restriction enzyme is a bacterial enzyme that cuts DNA, it creates fragments of DNA with “sticky ends”
- DNA ligase joins fragments together
- The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) uses the enzyme DNA polymerase to carry out multiple replications (a chain reaction) of
target DNA.
CRISPR-Cas9
-
Identifying the Target: CRISPR first identifies the specific sequence of DNA to be modified. This is done using a guide RNA molecule that matches the target DNA sequence.
-
Molecular Scissors: Once the target is identified, an enzyme called Cas9 (or other similar enzymes) acts like scissors, cutting the DNA at that precise location specified by the guide RNA.
-
Genetic Modification: When the DNA is cut, the cell's natural repair mechanisms come into play. Scientists can introduce changes to the DNA at this point by either letting the cell repair itself (which might result in random changes) or by providing a DNA template that the cell can use to make specific alterations.
-
Effect of Editing: This editing process can involve various modifications like removing certain sections of DNA, inserting new sequences, or even making precise changes to correct genetic mutations.
-
Functional Impact: These modifications can have significant effects, potentially correcting genetic diseases, enhancing specific traits in organisms, or allowing scientists to better understand the role of specific genes in biological processes.
Analyzing DNA Segments
1. Mitochondria DNA sequences in modern living populations can decipher the evolutionary history of human populations.
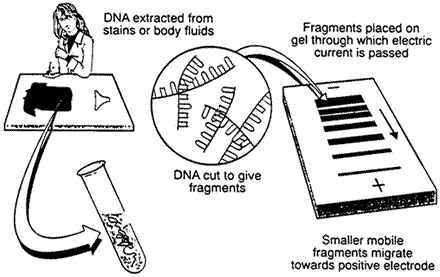
2. DNA fingerprinting is the technique of using DNA fragment lengths, resulting from restriction enzyme cleavage and amplified by PCR, to identify particular individuals.
a. DNA is treated with restriction enzymes to cut it into different sized fragments.
b. During gel electrophoresis, fragments separate according to length, resulting in a pattern of bands.
c. DNA fingerprinting can identify deceased individuals or perpetrators of crimes
3. PCR amplification and DNA analysis is used to:
a. detect viral infections, genetic disorders, and cancer;
b. determine the nucleotide sequence of human genes: the Human Genome Project; and
c. associate samples with DNA of parents because it is inherited.
Biotechnology Products
Transgenic Bacteria
1. Bacteria are grown in large vats where they can make products such as insulin and human growth hormone, and vaccines
2. Transgenic bacteria have been produced to improve the health of plants and degrade substances, such as oil
3. Transgenic bacteria can produce chemical products, such as phenylalanine (artificial sweeteners)
Transgenic Plants
1. Foreign genes now give cotton, corn, and potato strains the ability to produce insect toxin s
2. Plants are being engineered to produce human proteins including hormones, clotting factors, and antibodies
Transgenic Animals
Animal use requires methods to insert genes into eggs of animals (early in development). Using this technique, many types of animal eggs have been injected with bovine growth hormone (bGH) to produce larger fishes, cows, pigs, rabbits, and sheep.
Related Resources
Recombinant DNA Simulation - use paper and scissors to model DNA insertion of a target gene
