
Exploring Anatomy: A Comprehensive Guide to Fetal Pig Dissection Techniques and Observations
Fetal pigs share many anatomical similarities with humans. Studying fetal pig anatomy provides valuable insights into human anatomy, allowing students to understand structures and systems in a living organism. They are relatively affordable and easily obtainable for educational purposes. This accessibility makes them a practical choice for hands-on dissection activities in educational settings.
Fetal pigs are large enough to allow for detailed study of internal structures, yet small enough to be manageable for dissection in a classroom setting. Their stage of development is also suitable for observing various organ systems.
Fetal pig dissection allows for the exploration of multiple organ systems, including cardiovascular, respiratory, digestive, and reproductive systems. This versatility enhances the educational value of the dissectio
You can order fetal pigs from biological supply companies or from Amazon.
Studying the anatomy of a fetal pig through dissection allows students to explore these systems in detail and gain a better understanding of mammalian anatomy, including the similarities and differences with human anatomy.
The anatomy of a fetal pig is similar to that of other mammals, including humans. Here's an overview of key anatomical features in a fetal pig:
-
External Features:
- Size and Weight: Fetal pigs used in dissection are typically around 12-16 inches in length and weigh a few pounds.
- Eyes and Ears: Fetal pigs have well-developed eyes and ears.
- Limbs: Four limbs with hooves are present, and the skeletal structure is visible.
- External nares (nostrils) present
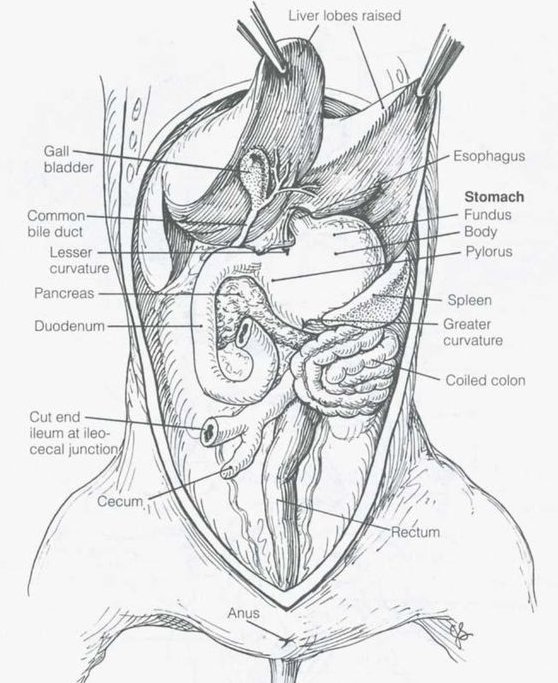
- Digestive System:
- Mouth: The mouth contains teeth for grinding food.
- Esophagus: Connects the mouth to the stomach.
- Stomach: Responsible for the initial digestion of food.
- Small Intestine: Absorbs nutrients from digested food; consists of three sections: duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
- Large Intestine (colon): Involved in water absorption and feces formation.
- Cecum: pouch at the junction of the ileum and colon
- Liver has many lobes and located just below the diaphragm, produces bile and breaks down substances
- Gallbladder is underneath the liver and stores bile; connect to liver via common bile duct
- Pancreas: located below the stomach, secretes insulin
- Respiratory System:
- Nose and Trachea: Air enters through the nose and travels down the trachea.
- Epiglottis: flap that closes during swallowing to prevent food from entering airway
- Lungs: Responsible for gas exchange (oxygen in, carbon dioxide out).
- Circulatory System:
- Heart: The heart is a four-chambered organ (two atria, two ventricles) that pumps blood.
- Aorta: Large artery that leaves the heart and supplies blood to the body
- Vena cava: Located next to the aorta, returns blood to the heart
- Blood Vessels: Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, while veins return deoxygenated blood to the heart.
- Urinary System:
- Kidneys: Filter blood and produce urine.
- Urinary Bladder: Stores urine before excretion.
- Reproductive System:
- Testes or Ovaries: Depending on gender, fetal pigs have either testes (male) or ovaries (female).
- In males, the scrotal sac is ventral to anus and contains the testes
- In females, the urogenital opening is ventral to anus, and has genital papilla
- Uterine horns are present internally in females
- Nervous System:
- Brain and Spinal Cord: Control and coordinate various body functions.
- Nerves: Extend throughout the body, transmitting signals.
- Skeletal System:
- Bones: The skeleton provides support and protection for internal organs.
- Bones: The skeleton provides support and protection for internal organs.
- Muscular System:
- Muscles: Muscles facilitate movement and contribute to the overall structure of the body.
- Muscles: Muscles facilitate movement and contribute to the overall structure of the body.
- Integumentary System:
- Skin: Covers and protects the body.
Fetal Pig Dissection Resources
Guide to the Fetal Pig Dissection – instructions for dissecting the fetal pig, includes external anatomy, major organs of the digestive, respiratory, circulatory and urinary system
Ultimate Fetal Pig Dissection Review – resources for studying
Fetal Pig Lab Guide – lists structures and check boxes
Gallery of the Fetal Pig – collection of labeled and unlabeled images, Google photos
Fetal Pig Flashcards (Quizlet) – practice identifying structures