Alternation of Generations
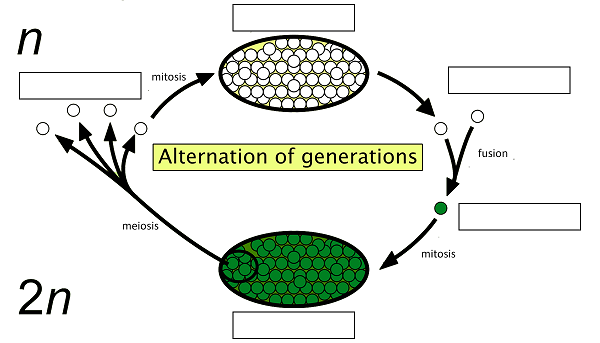
Alternation of Generations is a type of life cycle in plants and algae. It consists of a multicellular haploid sexual phase, the gametophyte. This phase alternates with a multicellular diploid asexual phase, the sporophyte..
A mature sporophyte produces haploid spores by meiosis. The haploid spores grow into multicellular haploid gametophytes. When those mature, they produce gametes by mitosis. Two haploid gametes fuse to produce a diploid zygote. This zygote then divides repeatedly to produce a multicellular diploid sporophyte. This cycle, from gametophyte to sporophyte (or equally from sporophyte to gametophyte), is the way in which all land plants and most algae undergo sexual reproduction.
Alternation of generations is a reproductive cycle found in plants where two different multicellular phases, the gametophyte and the sporophyte, alternate in their life cycle. This pattern occurs in plants like ferns, mosses, and certain algae.
-
Gametophyte Phase: This is the haploid (n) phase where gametes (eggs and sperm) are produced. It begins when haploid spores germinate and grow into multicellular structures called gametophytes. Gametophytes produce gametes through mitosis: male gametophytes produce sperm in specialized structures called antheridia, while female gametophytes produce eggs in structures called archegonia.
-
Fertilization: During fertilization, a sperm cell from the male gametophyte fertilizes an egg cell in the female gametophyte. This fusion of gametes creates a zygote, which marks the start of the next phase.
-
Sporophyte Phase: The zygote develops into a new multicellular structure called the sporophyte, which is diploid (2n). The sporophyte is dependent on the gametophyte for nutrients in some plant groups. It produces spores through a process called meiosis.
-
Spore Formation: The sporophyte undergoes meiosis to produce haploid spores. These spores are released and dispersed, and when they land in a suitable environment, they germinate and grow into new gametophytes, restarting the cycle.
In this alternation of generations, the diploid sporophyte produces haploid spores, which give rise to the haploid gametophyte, and the gametes produced by the gametophyte fuse to form the diploid sporophyte. This cycle continues, allowing for reproduction and the perpetuation of the plant species.
2. Haploid spores are produced by the [ sporophyte / gametophyte ]
3. A zygote is produced by the fusion of [ gametophytes / gametes ]
4. Spores reproduce by [ meiosis / mitosis ] to produce a gametophyte.
5. Sporophytes are [ diploid / haploid.] Gametophytes are [ diploid / haploid.]
6. A zygote is [ diploid / haploid.] . A spore is [ diploid / haploid.]
7. Sporophytes and gametophytes are both produced through the process of [ meiosis / mitosis ]
8. Which of the following is the best description of the process of alternation of generations? (Check all that apply)
__ a life cycle that includes a unicellular haploid stage
__ a life cycle that includes a unicellular diploid stage
__ a life cycle that includes a multicellular diploid stage
__ a life cycle that includes a multicellular haploid stage

