Human Heredity and Genetic Disorders

Human Chromosomes
Karyotype = picture or pattern of chromosomes arranged in homologous pairs & organized by size
Humans have 46 chromosomes
2 of these are sex chromosomes
XX = female XY = maleThe other 44 chromosomes are known as autosomes
Human Traits
To study inheritance, biologists use pedigree charts
Shows relationships within a family
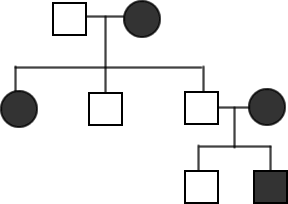
Pedigree studies are often used to track genetic disorders in a family.
Many traits are strongly influenced by environmental factors (ex: height,personality). The degree to which traits depend on genetics is called HERITABILITY
Human genome
Our complete set of genetic info , Includes tens of thousands of genes
Genes are mapped to chromosomes.
Used to determine how traits or diseases are inherited.
Example: BRCA1 is located on chromosome 17, it is associated with risk of breast cancer.
ABO Blood Group
Controlled by 3 alleles - A, B, O
A and B are codominant
O is recessive to both A and B
The blood type is the phenotype
| Blood Type | Genotype | Can Donate to... | Can Receive from... |
|
AA, AO | A or AB | A or O |
 |
BB, BO | B or AB | B or O |
 |
AB | AB only | A or B or AB (universal receiver) |
 |
OO | A, B, AB, O (universal donor) |
Only O |
Human Genetic Disorders
Recessive
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Tay - Sachs disease recessive
Albinism
Cystic Fibrosis
Dominant
Achondroplasia
Huntington's disease
Polydactyly
Codominant
Sickle-cell disease
*Also gives resistance to malaria
Blood types (A and B are codominant)