Frog Anatomy and Dissection Images

Head and Mouth Structures
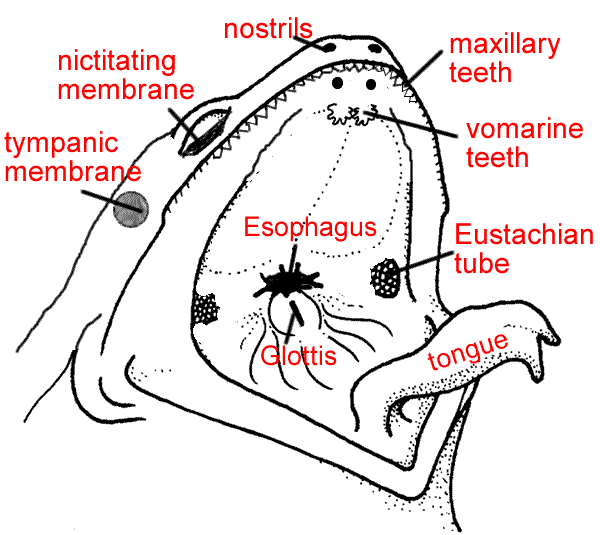
Vomerine Teeth: Used for holding prey, located at the roof of the mouth
Maxillary Teeth: Used for holding prey, located around the edge of the mouth
Internal Nares (nostrils) breathing, connect to lungs
Eustachian Tubes: equalize pressure in inner ear
Glottis : Tube leading to the lungs
Esophagus: Tube leading to the stomach
Tongue: Front attached, aids in grabbing prey
Tympanic Membrane: eardrum, located behind eyes
Nictitating Membrane: clear eyelid, protects the eye
The Organs of the Abdominal Cavity
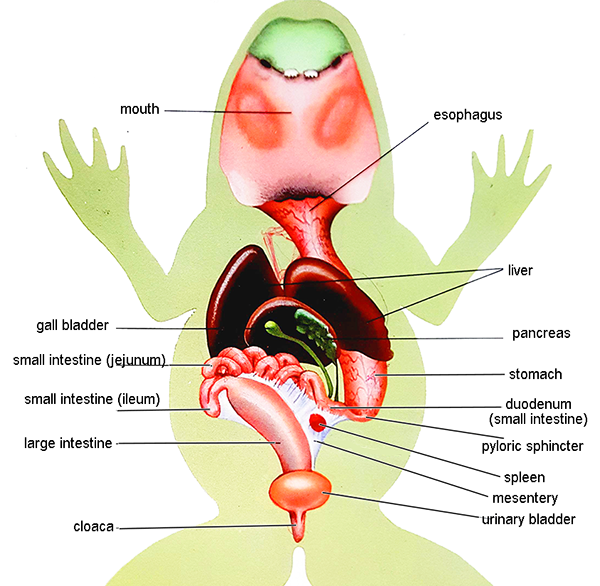
Peritoneum: Spiderweb like membrane that covers organs
Stomach: First site of chemical digestion, breaks down food
Pyloric Sphincter - valve between stomach and small intestine
Liver: Makes bile (aids in digestion)
Gall bladder: Stores bile
Esophagus: Tube that leads to the stomach
Pancreas: Makes insulin (aids in digestion)
Small Intestine (duodenum, jejunum and ileum): absorb nutrients from food
Mesentery: Holds coils of the small intestine together
Large Intestine: Collects waste, absorbs water
Cloaca: "Sewer": eggs, sperm, urine and feces enter this area
Spleen: Part of circulatory system, stores blood
The Urogenital System
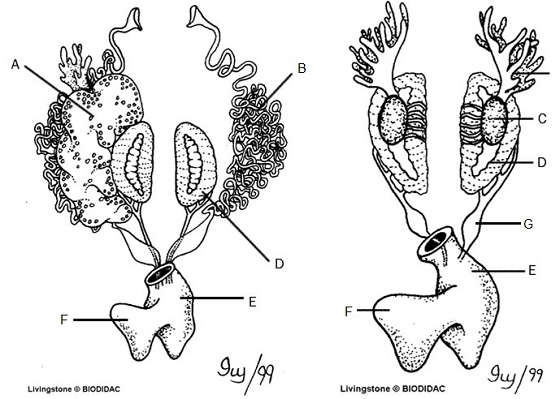
Kidneys (D): Filter Blood
Ureters (G): Carry urine from kidneys to bladder
Testes (C): Make sperm
Oviducts (B): eggs travel through these
Ovary: makes eggs (A) - ovary is often too small to see, but eggs are visible
Urinary Bladder (F): Stores Urine
Cloaca (E): Where sperm, eggs, urine, and feces exit.
