Genetics Review Sheet - Final Exam

1. A person with type AB blood could
receive what type of blood?_________________
2. The study of heredity is called ________________________
3. DNA is an abbreviation for ___________________________________
4. The "Father of Genetics": ____________________________
5. A diagram that is used to predict the outcome of a genetic cross _________________
6. A persons external appearance is the [ genotype / phenotype ]
7. Disease known as "bleeder's disease" ________________________
8. Traits being passed from parents to offspring is called ___________________
9. Mendel did his research using ____________ plants.
10. An alternate form of a gene is called an ______________________.
11. The shape of a DNA molecule is a ____________________________
12. Genes located on sex chromosomes are called ______________________
13. A person with two X chromosomes XX will be [ male / female ]
14. A person with type O blood can receive what type of blood? ___________
15. A cross that involves only one pair of contrasting traits [ monohybrid / dihybrid ]
16. Give an example of two polygenic traits _________________________
17. What disease causes an inability of the blood to clot _____________________
18. Mendels first generation, after the parental generation was called ___________
19. A carrier is a person who is [ heterozygous / homozygous ]
20. A segment of DNA that controls a particular trait __________________
21. Which of the following represents a homozygous genotype: [ AA / Aa ]
22. Name a sex-linked disease ________________________
23. If a yellow seeded plant is crossed with a green seeded plant, and all of
the offspring are green, which trait is dominant [ yellow / green ]
24. A family record that shows how a trait is inherited over several generations
is called a ___________________
Genetics Problems
1. In some flowers, red and white color is codominant. Flowers and be red (RR), white (rr) or pink (Rr)
If two pink flowers are crossed, what percentage of the offspring will also be pink?
If a red and a white flower are crossed, what percentage of the offspring will
be pink?
2. A man who has normal vision X Y is married to a woman who is colorblind. X X
How many of their children will be colorblind and what is their sex?
3. In pea plants, tall is dominant
to short.
A heterozygous tall (Tt) is crossed with a short (tt) plant. What percentage
of their offspring will be short?
Two short plants are crossed, what percentage of their offspring will be short?
Two heterozygous plants are crossed, what percentage of their offspring will be tall?
4. A man with type AB blood is married to a woman with type AB blood. What blood
types are possible among their children and in what proportion?
5. A man with type O blood is married to a woman with type A blood (she can
be either genotype AO or AA). What blood types are possible among their children?
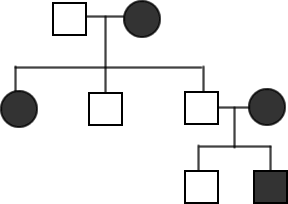
6. Determine the genotypes in the pedigree below. The trait being studied is
the tongue rolling ability. Those who cannot roll their tongue are recessive
(tt)