Taxonomy - The Science of Classifying

Classification - organizing life forms into groups
Why classify? Common Names can be misleading
| spider monkey | sea monkey |
| gray wolf | firefly |
| mud puppy | horned toad |
| black bear | jellyfish |
| ringworm | crayfish |
| sea horse | frogfish |
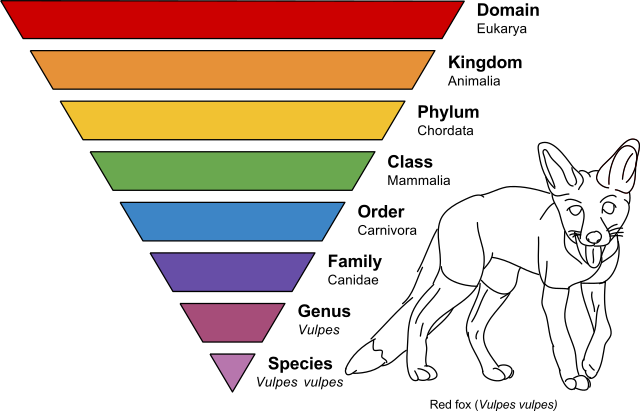
Linneaus - devised the current system of classification, which uses the following schema (Domain was added later)
Domain - Kindgom - Phylum - Class - Order - Family - Genus - Species
(Dear King Philip Came Over For Great Soup)
Binomial Nomenclature - Two Name System
-written in italics (or underlined)
-1st word is Capitalized --Genus
-2nd word is lowercase ---speciesExamples: Felis concolor, Ursus arctos, Homo sapiens, Panthera leo , Panthera tigris
The scientific name is always italicized or underlined. Genus is capitalized. Species is not. Scientific names can be abbreviated by using the capital letter of the genus and a period: Example. P. leo (lion)
Examine how these animals are organized into the different groups:
| Human | Cougar | Tiger | Pintail Duck | |
| Kingdom | Animalia | Animalia | Animalia | Animalia |
| Phylum/Division | Chordata | Chordata | Chordata | Chordata |
| Class | Mammalia | Mammalia | Mammalia | Aves |
| Order | Primate | Carnivora | Carnivora | Anseriformes |
| Family | Homindae | Felidae | Felidae | Anatidae |
| Genus | Homo | Felis | Panthera | Anas |
| Species | sapiens | concolor | tigris | acuta |
The Six Kingdoms and Domains
| number of Cells | energy | cell type | examples | |
| archaebacteria | unicellular | some autotrophic, most chemotrophic | prokaryote | "extremophiles" |
| eubacteria | unicellular | autotrophic and heterotrophic | prokaryote | bacteria, E. coli |
| fungae | most multicellular | heterotrophic | eukaryote | mushrooms, yeast |
| plantae | multicellular | autotrophic | eukaryote | trees, grass |
| animalia | multicellular | heterotrophic | eukaryote | humans, insects, worms |
| protista | most unicellular | heterotrophic or autotrophic | eukaryote | ameba, paramecium, algae |
Modern Classification System
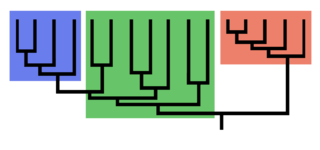
Phylogeny - studies evolutionary relationships
Clade - a group the includes a single common ancestor
Cladogram - diagram that shows clades and how they are linked by shared traits
Derived character - a trait that arose in a common ancestor; all descendants share this trait