The Chemistry of Life
Anchoring Phenomenon: Why Did Sailors Get Scurvy?
2.1 The Nature of Matter
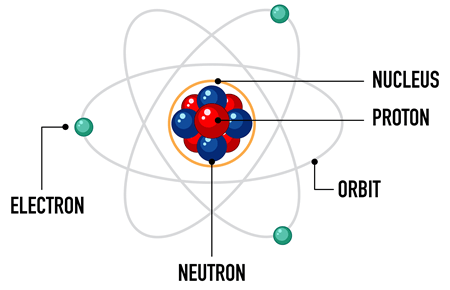
Atoms
-protons (positive)
-electrons (negative)
- neutrons (no charge)
Elements
-consist of only one type of atom
- Examples: Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
Compounds
-consist of two or more elements
- Examples: Water, table salt
- shows elements arranged by their atomich number
Chemical Bonds
- ionic (transferring of electrons)
- covalent (sharing electrons)
Interactions between atoms and molecules
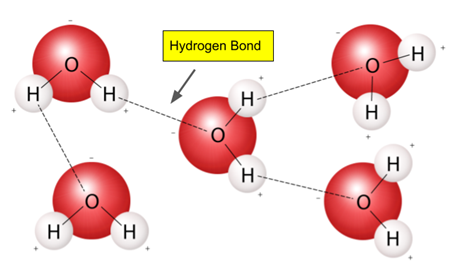
- hydrogen bonds (water)
- van der Waals forces (gecko feet)
2.2 Properties of Water
Video: Why Water Striders Make Terrible Lifeguards
1. Polarity
- water has a partial positive and partial negative charge
- it is a polar molecule
- forms hydrogen bonds (weak)
2. Cohesion
- surface tension (water is "sticky")
- allows some insects to walk on water
3. Adhesion
- water sticks to other things
- capillary action
4. Heat Capacity
- the amount of energy needed to change temperature
- water absorbs heat
- the surface of water can freeze, leaving liquid water underneath (for fish)
5. Universal Solvent
- many substances dissolve in water
- solutes are things that dissolve (like salt)
- creates a solution
6. Occurs in Three States
- gas (water vapor)
- liquid (pond, oceans)
- solid (ice)
* Frozen water is less dense than liquid water, so ice floats!
Water in Living Things
- organisms are mostly water
- the body's chemical reactions are dependent on water
Investigation: Water and Surface Tension
2.3 Carbon Compounds
- organic compounds (chains of carbon)
- macromolecules (large molecules)
Carbohydrates
- monosaccharides (simple sugars)
- polysaccharides (complex, multi chain sugars)
- glycogen for energy storage in animals
- starch for energy storage in plants
- cellulose for plant structure
Nucleic Acids
- information storage
- DNA
- RNA
Proteins
- made of amino acids
- joined by peptide bonds
- example: hemoglobin
2.4 Enzymes
- speed chemical reactions that take place in cells
- Lactase is an enzyme that helps us digest milk (Lactose)
Example of Enzyme Reaction
Enzymes interact with substrates, resulting in products
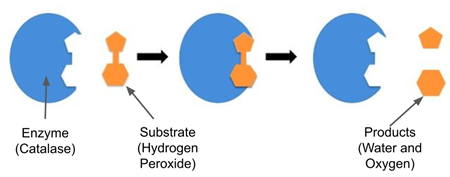
Catalase + Hydrogen Peroxide --> Water and Oxygen
Oxygen creates bubbles!
Enzymes work best at OPTIMAL temperatures
Enzymes also have an OPTIMAL pH (measure of acidity)