The Peripheral Nervous System
Peripheral Nervous System - consists of the nerves that branch out from the CNS and connect it to other body parts, also includes the cranial nerves
Somatic Nervous System (conscious activities)
- skin, skeletal systemAutonomic Nervous System (unconscious activities)
- heart, viscera, glands
CRANIAL NERVES (12 pairs)
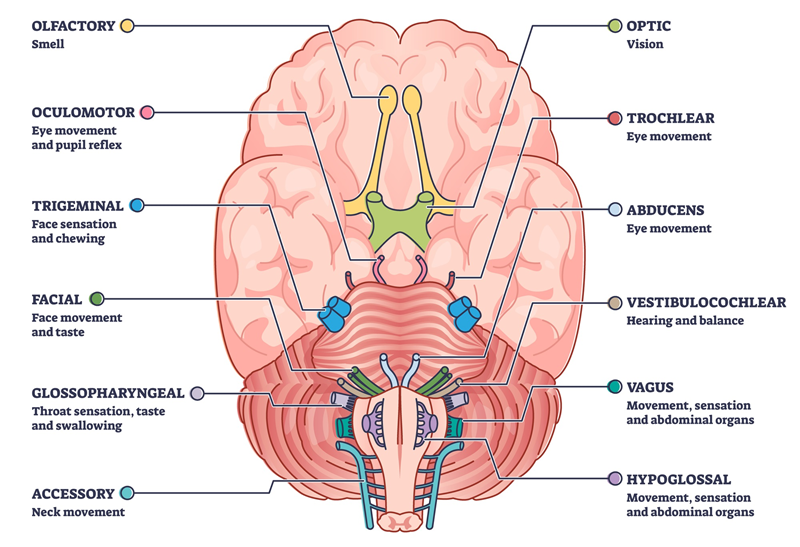
-
Olfactory (I): This nerve is associated with the sense of smell. It transmits information about odors from the nose to the brain.
-
Optic (II): The optic nerve is crucial for vision, carrying visual information from the eyes to the brain's visual centers.
-
Oculomotor (III): Responsible for controlling most eye movements and pupil constriction, this nerve helps in focusing and controlling the position of the eye.
-
Trochlear (IV): This nerve controls the superior oblique muscle of the eye, aiding in downward and inward eye movement.
-
Trigeminal (V): One of the largest cranial nerves, the trigeminal nerve has sensory functions for the face, including touch, pain, and temperature sensations, as well as controlling the muscles used for chewing.
-
Abducens (VI): This nerve controls the lateral rectus muscle of the eye, aiding in outward eye movement.
-
Facial (VII): Responsible for facial expressions, taste sensation from the front two-thirds of the tongue, and controlling tear and saliva production.
-
Vestibulocochlear (VIII): Also known as the auditory or acoustic nerve, it's associated with hearing and balance, transmitting information from the inner ear to the brain.
-
Glossopharyngeal (IX): Involved in taste sensation at the back of the tongue, swallowing, and sensory information from the throat and back of the tongue.
-
Vagus (X): The vagus nerve is incredibly important, influencing the heart rate, digestion, and various other involuntary bodily functions. It also plays a role in speech and swallowing.
-
Accessory (XI): This nerve controls certain muscles in the neck, particularly those used for head movement and shoulder shrugging.
-
Hypoglossal (XII): Responsible for controlling the muscles of the tongue, aiding in speech and swallowing.
 There is a mnemonic to help you remember the 12 cranial nerves:
There is a mnemonic to help you remember the 12 cranial nerves:
On Old Olympus Towering Top, A Finn And German Viewed A Hop
Each letter corresponds with the first letter of the cranial nerves.
SPINAL NERVES (31 pairs)
These are not named individually, they are grouped according to the level from which they arise
8 pairs of cervical nerves (C1 -
C8)
12 pairs of thoracic nerves (T1-T12)
5 pairs of lumbar nerves (L1-L5)
5 pairs of sacral nerves (S1-S5)
1 pair of coccygeal nerves (Co)
*Spinal cords ends at the level between
the 1st and 2nd lumbar vertebrae
*The lumbar, sacral, coccygeal nerves descend from the end of the cord - CAUDA
EQUINA (horse's tail)