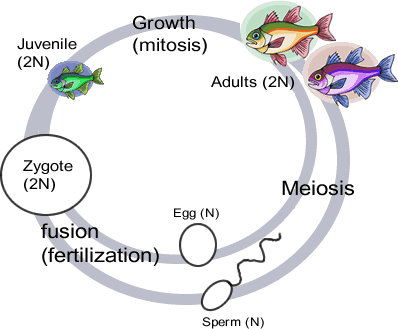
10.1 Meiosis
-the production of haploid cells with unpaired chromosomes - word
means "to diminish"
-process creates gametes (sperm and eggs), cells that are haploid (1N)
-gametes can combine to create a zygote which is diploid (2N)
Chromosome Structure
Each chromosome has mane alleles, or alternate forms of genes
Homologous Chromosomes - each chromosome has a match, called a homolog
Human Karyotype - chromosomes are numberd and paired according to size and banding pattern
Diploid vs Haploid
Body cells have the full set of chromosomes – they are DIPLOID (2N)
Sex cells (sperm and eggs) have half a set – they are HAPLOID (1N)
*In humans, each sperm contains 23 chromosomes, each egg contains 23 chromosomes; zygote has 46
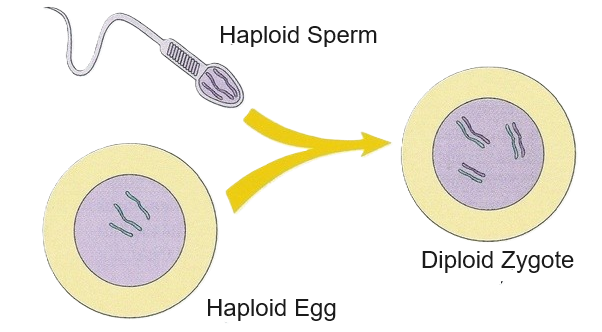
10.2 Genetic Variation
Crossing-Over - during prophase I, homologous pairs join together (synapsis) and exchange genetic information, chromatids are no longer exact duplicates
During metaphase, chromosomes line up in PAIRS, randomly – a phenomenon known as INDEPENDENT ASSORTMENT

Fertilization = combining the genes of two different parents, offspring contain variation due to crossing over and independent assortment
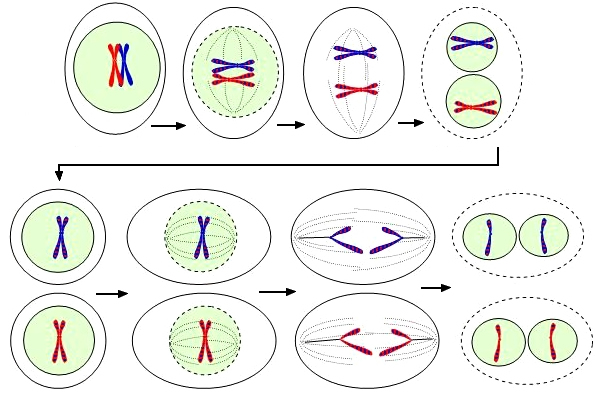
10.3 The Phases of Meiosis
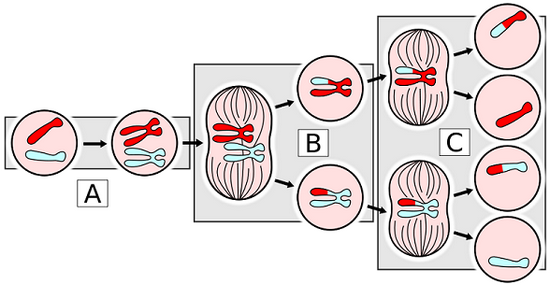
Key points of Meiosis
-The process results in 4 daughter cell
-daughter cells are haploid (N)
- cells have unique combinations of chromosomes|
- cells do not have homologous pairs
- Meiosis creates gametes (sperm and eggs)
10.4 Meiosis Compared to Mitosis
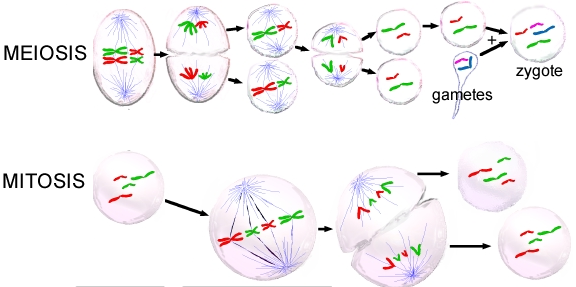
Steps of Meiosis
10.5 The Human Life Cycle
GAMETOGENESIS - process of creating gametes
Oogenesis
- Meiotic arrest occurs during prophase I until puberty. At puberty, meiosis I resumes, but meiosis II halts until fertilization.
- Yields larger and less mobile gametes (eggs) due to the need to provide nutrients and cellular material for early embryonic development.
Spermatogenesis
- Meiosis continuously progresses without interruption after puberty, resulting in the constant production of sperm cells.
- Produces smaller, highly motile gametes (sperm) designed for efficient movement to reach and fertilize an egg.
Types of Sexual Life Cycles
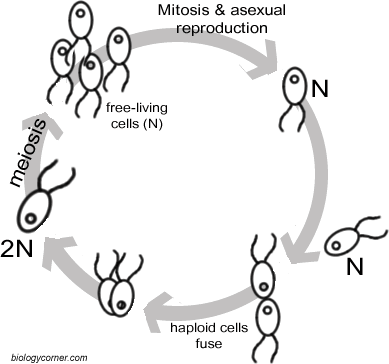
Haploid Life Cycle
-
Haploid Stage (n): In the haploid life cycle, the dominant phase of the organism's life is haploid. Organisms start with haploid cells that contain only one set of chromosomes.
-
Mitosis: Haploid cells divide by mitosis, a type of cell division that duplicates the chromosomes and results in identical daughter cells with the same chromosome number (haploid).
-
Fusion and Zygote Formation: Haploid cells may come together, fuse, and form a diploid zygote. This zygote then directly undergoes meiosis to produce haploid cells, completing the cycle.
-
Example: Fungi, algae, and some plants have life cycles where the dominant phase is haploid. For instance, in some fungi, the main body (mycelium) is haploid, and when two compatible haploid cells fuse, they form a diploid zygote that immediately undergoes meiosis to produce haploid spores.
Diploid Life Cycle
-
Diploid Stage (2n): In the diploid life cycle, organisms start with cells that have pairs of homologous chromosomes, one inherited from each parent. These cells are diploid (2n) because they contain two sets of chromosomes.
-
Meiosis: During the process of sexual reproduction, diploid cells undergo meiosis, a specialized type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half. Meiosis results in the formation of haploid cells.
-
Haploid Gametes: The end result of meiosis is the formation of haploid gametes (sperm cells in males and egg cells in females), each containing only one set of chromosomes.
-
Fertilization: When these haploid gametes from two parents fuse during fertilization, they form a diploid zygote. The zygote then develops into a new diploid organism, restarting the diploid phase of the life cycle.
-
Example: In humans, all somatic (body) cells are diploid, containing 46 chromosomes (23 pairs). These cells undergo meiosis in the gonads (testes in males, ovaries in females) to produce haploid gametes (sperm and egg cells).