Photosynthesis - How Does It Work?
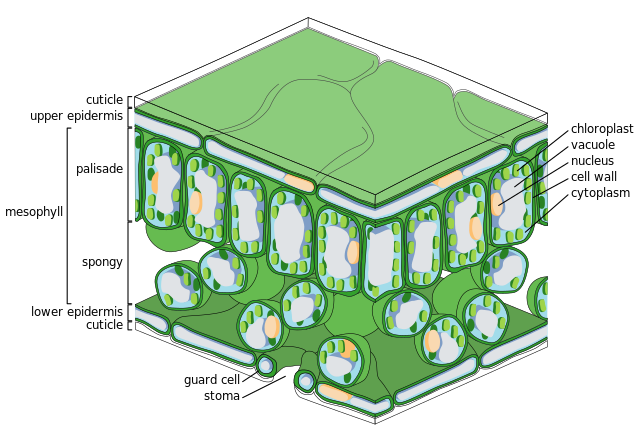
Structure of a Leaf
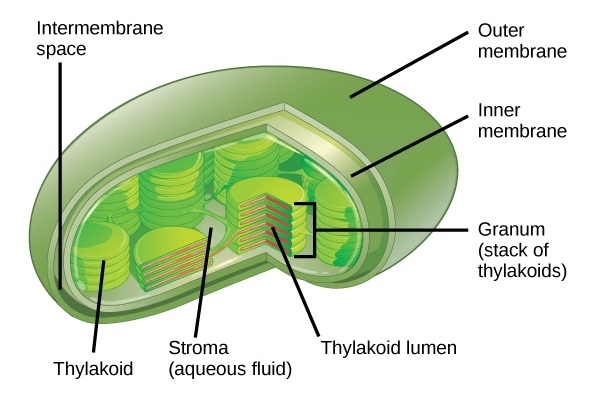
Structure of a Chloroplast
Plants as Solar Energy Converters
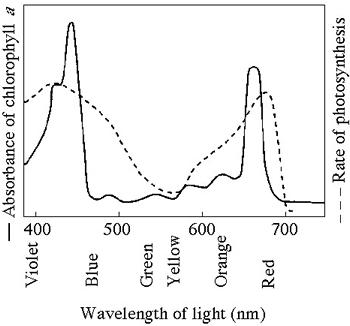
Photosynthetic Pigments - Pigments found in chlorophyll absorb various portions of visible light; absorption spectrum.
1. Two major photosynthetic pigments are chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b.
2. Both chlorophylls absorb violet, blue, and red wavelengths best.
3. Very little green light is absorbed; most is reflected back; this is why leaves appear green.
4. When chlorophyll breaks down in fall, the yellow-orange pigments (carotenoids) in leaves are visible.
Absorption Spectrum - A spectrophotometer measures the amount of light that passes through a sample of pigments.
Action Spectrum - measures the rate of photosynthesis at different wavelengths of light; measured by the rate oxygen is produced
The Action and Absorption Spectrum can be combined into one handy graph. In one sentence summarize what this graph says about wavelengths, color of light, absorption and photosynthesis.
Photosynthetic Reaction
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Ted Talks Video: What is the relationship between photoysnthesis respiration?
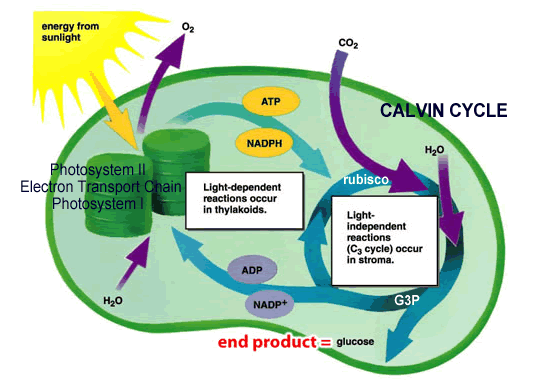
Two Sets of Reactions in Photosynthesis (Light Reaction & Calvin Cycle)
1. Light reactions are the energy-capturing reactions, requires energy from the sun
a. Occurs in the thylakoid, water is split
b. ATP and NADPH are produced to power the Calvin Cycle
c. Oxygen is released
2. Calvin Cycle Reactions (Light Independent Reactions)
a. These reactions take place in the stroma; can occur in either the light or the dark.
b. These are synthesis reactions that use NADPH and ATP (from the Light Reaction) to reduce CO2.
c. The end product is glucose which can be used by the plant
The Light Reactions occurs in two systems: Photosystem I and II - the creation of ATP is a complicated process
You will take a closer look at Photosystem I and Photosystem II in the Photosystem Coloring Worksheet