CELLULAR RESPIRATION - LAB BASED GUIDE
*AP Biology LAB 5 - Complete the data gathering and graphing first.
1. What is the purpose of KOH? What would happen if you forgot to soak the cotton in KOH?
2. What is the micropipette measuring in your peas?
3. How do you determine the rate of respiration using a respirometer? Could you sketch a respirometer?
Big Idea: Cellular respiration and fermentation harvest free energy from sugars to produce free energy carriers (ATP.) The energy in sugars drives metabolic pathways in cells. Photosynthesis and respiration are interdependent processes. Cellular respiration is the breakdown of glucose (C6H12O6) in the presence of oxygen (O2) to produce cellular energy - ATP
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6 CO2 + 6H2O + 36 ATP
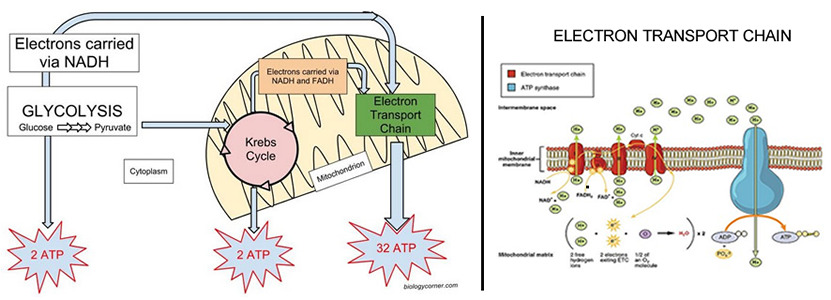
Summary of Graphic
A. Glycolysis rearranges bonds in glucose, releasing ATP and producing pyruvate | B. Pyruvate moves to the mitochondria, where it is used in the Krebs Cycle
C. In the Krebs cycle, carbon dioxide is released and 2 ATP synthesized. | D. The Krebs cycle also produces NADH and FADH2 which are used in the electron transport chain
E. The electron transport chain produces 32 ATP
(chemiosmosis)
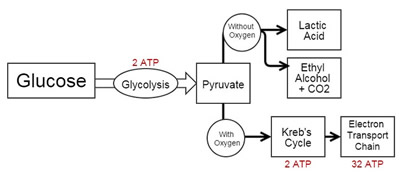
Anaerobic Respiration - without oxygen (fermentation)
Food for Thought
1. Where does cellular respiration occur within the cell? What is the purpose of cellular respiration?
2. Why is oxygen necessary? What happens when oxygen is not available?
3. How are photosynthesis and cellular respiration related?
a) What are the equations of each?
b) Describe the role of ATP Synthase in photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
4. (BIG QUESTION) When you walk your dog, you are using energy from the sunlight to power this activity. Explain.
5. (BIG QUESTION) Bacteria do not have mitochondria. How do they obtain their energy? Can bacteria survive without oxygen?
6. (BIG QUESTION) Biology is all about modeling processes we can't actually see. Can you model cellular respiration?