DNA and the Central Dogma
Anchoring Phenomenon: How Can Small Changes in DNA Cause Big Changes in Organisms?

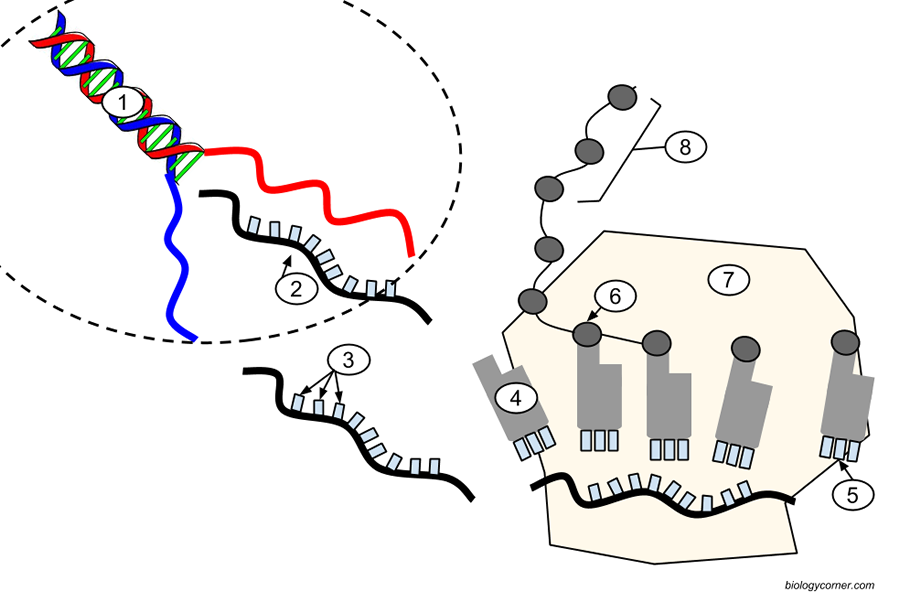
The central dogma of molecular biology describes the flow of genetic information within a biological system, primarily involving the transfer of information from DNA to RNA to proteins. It's a fundamental concept that outlines how genetic instructions are converted into functional molecules within the cell.
-
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid): It serves as the repository of genetic information in a cell. DNA contains genes, which are sequences of nucleotides that encode specific instructions for creating proteins.
-
Transcription: The first step in the central dogma is transcription, where a segment of DNA is used as a template to create a complementary RNA molecule. This process occurs in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells. The enzyme RNA polymerase catalyzes the formation of RNA by assembling ribonucleotides based on the DNA template.
-
RNA (Ribonucleic Acid): The transcribed RNA molecule (known as messenger RNA or mRNA) carries the genetic information from the DNA to the ribosomes, which are the cellular machinery responsible for protein synthesis.
-
Translation: In the cytoplasm, specifically on ribosomes, the mRNA is used as a template to synthesize proteins. Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules ferry amino acids to the ribosome according to the mRNA sequence. The sequence of nucleotides in the mRNA is translated into a specific sequence of amino acids, forming a polypeptide chain, which then folds into a functional protein.
To summarize, the central dogma illustrates the unidirectional flow of genetic information: from DNA (through transcription) to RNA and finally to proteins (through translation). This flow of information is crucial for the synthesis of proteins, which are the key players in most cellular functions and processes.
Guiding Questions
1. What is the LMNA gene?
2. What is the relationship between genes and proteins and enzymes?
3. What is the central dogma?
4. How does RNA differ from DNA?
5. What is a codon? How are codon charts used?
6. What is transcription?
7. What is translation?
8. Model the process of transcription and translation