Simple Genetics Practice Problems KEY
This worksheet will take about 20 minutes for most students, I usually give it to them after a short lecture on solving genetics problems. I don't normally take a grade on it, instead just monitor progress of students as they work and then have them volunteer to write the answers #5-15 on the board.
1. For each genotype, indicate whether it is heterozygous (HE) or homozygous (HO)
|
AA _HO__ |
Ee _HE___ ff _HO___ GG _HO__ HH _HO__ |
Ii __HE__ Jj __HE__ kk _HO___ Ll _HE___ |
Mm _HE___ nn _HO__ OO _HO__ Pp _HE___ |
2. For each of the genotypes below, determine the phenotype.
|
Purple flowers are dominant
to white flowers |
Brown eyes are dominant to
blue eyes BB ___brown____ Bb ___brown___ bb ___blue_____ |
|
Round seeds are dominant
to wrinkled |
Bobtails are recessive (long
tails dominant) |
3. For each phenotype, list the genotypes. (Remember to use the letter of the dominant trait)
| Straight hair is dominant
to curly. _____SS______ straight _____Ss_____ straight _____ss_____ curly |
Tail spikes are dominant to plain ____TT____ pointed ____Tt______ pointed ____tt_______ round |
4. Set up the square for each of the crosses listed below. The trait being studied is round seeds (dominant) and wrinkled seeds (recessive)
|
Rr x rr
|
What percentage of the offspring will be round? ___1/2 or 50%___ | |
|
Rr x Rr
|
What percentage of the offspring will be round? ___75% or 3/4_ | |
|
RR x Rr
|
What percentage of the offspring will be round? __all, 100%_____ |
Practice with Crosses.
0I've only included a couple of squares as samples here, most of these are very straightforward. Given enough practice, students will learn to do most of them without the squares.
5. A TT (tall) plant is crossed with
a tt (short plant).
What percentage of the offspring will be tall? _____all tall_____
6. A Tt plant is crossed with a Tt
plant. What percentage
of the offspring will be short? ___25%__
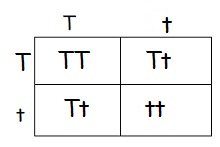
7. A heterozygous round seeded plant
(Rr) is crossed with a
homozygous round seeded plant (RR). What percentage of
the offspring will be homozygous (RR)? ____1/2 or 50%______
8. A homozygous round seeded plant
is crossed with a homozygous
wrinkled seeded plant. What are the genotypes of the parents?
_____RR____ x ___rr______
What percentage of the offspring will also be homozygous? _____0%_____
9. In pea plants purple flowers are
dominant to white flowers.
If two white flowered plants are cross, what percentage of their
offspring will be white flowered? _____all white_______
If students are stuck on this one, advise them to make a "key" to help them sort it out.
PP = purple, Pp = purple, pp = white
10. A white flowered plant is crossed
with a plant that is
heterozygous for the trait. What percentage of the
offspring will have purple flowers? _____pp x Pp, 50% purple_____
11. Two plants, both heterozygous
for the gene that controls
flower color are crossed. What percentage of their offspring
will have purple flowers? Pp x Pp , 75% purple______________
What percentage will have white flowers? ____25% white_______
12. In guinea pigs, the allele for
short hair is dominant.
What genotype would a heterozygous short haired guinea pig have? __Hh___
What genotype would a purebreeding short haired guinea pig have? __hh____
What genotype would a long haired guinea pig have? __HH____
Why did I use H instead of S for short hair. Students may discover the hard way that capital and lower case S's are hard to tell apart. This is a good time to talk to them about how to choose their letters. You can choose the letter of the dominant trait, or you can chooe the letter for the trait itself (H is for hair).
. Show the cross for two heterozygous
guinea pigs. Hh x Hh
What percentage of the offspring will have short hair? __75%____
What percentage of the offspring will have long hair? __25%_____