Meiosis
-
the process of nuclear division where the number of the chromosomes is halved.
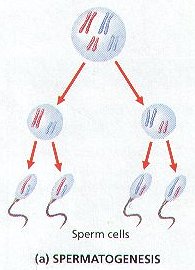
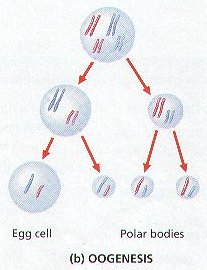
- produces four daughter cells
- all daughter cells are haploid
- chromosomes are shuffled in the process, so that each daughter cell has a unique combination
- used to create gametes (sperm and egg)
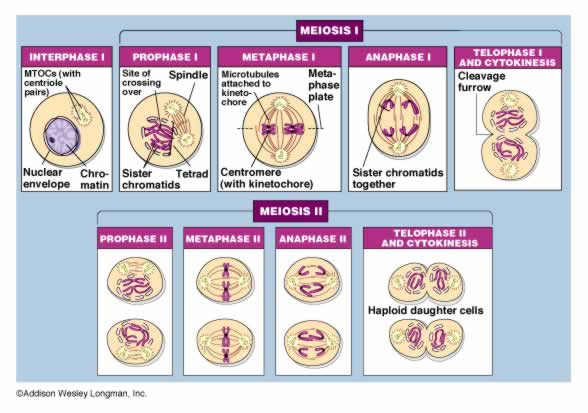
Prophase 1
- homologous chromosomes pair up (tetrad)
- crossing-over occurs
Metaphase & Anaphase
- tetrads line up along the equater, homologs separate
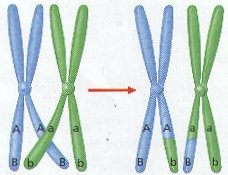
Crossing Over - chromosomes exchange sections (increases variability)
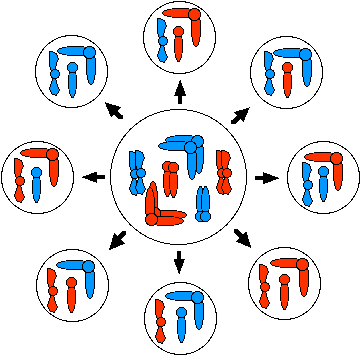
Independent Assortment
In addition to Crossing-Over, the process of meiosis ensures that chromosomes are randomly assorted. The following images show three separate possibility for a single cell that has undergone meiosis. Look at all the different combinations.
|
Sexual Reproduction - Involves the fusion
of gametes, creates unique offspring
|
Image of egg and sperm |
Asexual Reproduction
--Does not involve the fusion
of gametes
--Offspring are identical to parents
--Budding, Fragmentation (Regeneration), Fission