Final Exam Review Guide

Overview: 5 sections, 130-150 multiple choice questions
Comprehensive; covers all topics learned in Biology 1(1A)
Worth 20% of your overall grade
Section A: Scientific Processes and Introduction to Biology (Ch 1)
Topics: Microscope Use, Scientific Method, Metric System
1. List the steps of the scientific method:
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
________________________________________________
_______________________________________________
2. Understand how a controlled experiment is conducted.
Sample: A scientist wants to know if Miracle Grow will increase the number of tomatoes on his tomato plants. To tomato plant A he adds miracle grow; and to tomato plant B he does not add miracle grow. Both plants are given the same amount of light and water. After 6 weeks he counts the number of tomatoes are present on each plant. Plant A = 9 Plant B = 4
a. What is the manipulated variable in the experiment?____________
b. What is the responding variable? ________________
c. Which is the control group? _________
3. Microscope Use:
a. When first focusing the microscope, which objective do you use? __________
b. When using the high power objective, which focus knob do you use? ____________
c. What are the three objectives found on the microscopes you used in class? ______
d. What part of the microscope can be used to adjust the amount of light? _____
4. Metric System
a. What metric system unit would be used to measure volume (such as a can of coke) ? _________
b. What metric system unit would be used to measure the length of a room? ___________
5. Terms/Concepts
a. Biology ________________________________________________________________________
b. Science ________________________________________________________________________
c. Hypothesis ________________________________________________________________________
d. Controlled Experiment _________________________________________________________________
e. Cell ________________________________________________________________________
f. Organism ________________________________________________________________________
g. Louis Pasteur ________________________________________________________________________
h. Spontaneous Generation ________________________________________________________________
i. Homeostasis ________________________________________________________________________
j. Responsiveness ________________________________________________________________________
k. Reproduction ________________________________________________________________________
l. Evolution ________________________________________________________________________
m. Energy ________________________________________________________________________
n. Observations ________________________________________________________________________
o. Theory ________________________________________________________________________
Section B: Cells and Cell Processes (Ch 7)
Topics: Cell Structure, Organelles, Types of Cells, Cell Transport, Cell Division
1. What structure distinguishes a eukaryote from a prokaryote? ______________________
2. What shape is a plant cell? ____________ An animal cell? _______________________
3. What part of the cell is described as selectively permeable? ______________________
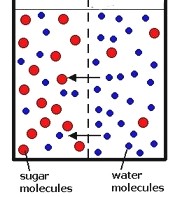
4. If you place a few drops of food coloring in a glass full of water, eventually all the water is colored. This is due to the process of ______________________
5. For each of the structures listed, indicate whether it is found in PLANTS (P), ANIMALS (A), or BOTH (B)
_____ Chloroplasts ______ Cell Membrane ______ Nucleus ______ Cell Wall ______ Mitochondria
6. In each of the situations pictured, indicate whether the cell will gain water, lose water, or stay the same. In each case, the cell in the beaker is 10% salt.
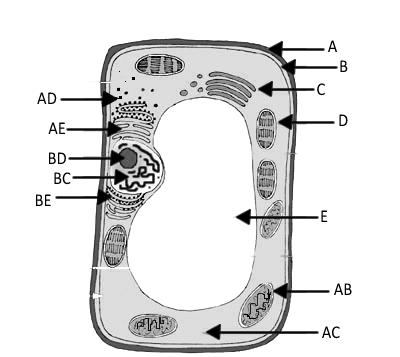
7. Know the function of each of the cell organelles listed:
a. Endoplasmic Reticulum ________________________________________________
b. Cell Membrane ________________________________________________________
c. Ribosome ________________________________________________________
d. Lysosome ________________________________________________________
e. Nucleus ________________________________________________________
f. Mitochondria _____________________________________________________
g. Golgi Apparatus __________________________________________________
8. Identify the process pictured as either mitosis, osmosis, or endocytosis
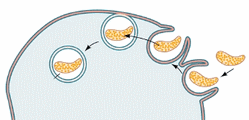
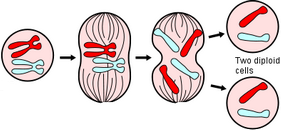
Bio 1A: Also identify the phases of mitosis
9. Label a plant and an animal cell:
Section C: Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration (Ch 8 & Ch 9)
1. How does ATP store and release energy? _____________________________________
2. Why do plants appear green? _________________________________________
3. What are the reactants and products of Photosynthesis? (write equation)
4. In plants, where does photosynthesis take place? ________________________
5. What affects the rate of photosynthesis? _______________________________
6. What is an autotroph? _________________________________
7. The light independent reation is also called the ________________ Cycle.
Respiration
1. Glycolysis releases only a small/large amount of energy if oxygen is not present. Circle One
2. Both plant and animal cells carry out the final stages of cellular respiration in the ______________________________.
3. _____________ _______________ is the process that releases energy by breaking down food molecules in the presence of oxygen.
4. Where in the cell does glycolysis take place? __________________________________________________________
5. Complete the equation for cellular respiration:
6O2 + ______________ 6CO2 + ________ + _____________
6. ______________ is the process in which one molecule of glucose is broken in half, producing two molecules of pyruvic acid, a 3-carbon compound.
7. What net gain in ATP molecules does the cell get during the process of glycolysis? ____________________________
8. If oxygen is not present in glycolysis, what is the name of the different pathway it takes? ______________________
9. Aerobic respiration uses one molecule of glucose to produce a total of ____ ATP.
10. Glycolysis take place where in the cell and under what circumstances? __________________________________
11. Gycolysis produces ______ ATP
Section D: Evolution and Taxonomy
Topics: Classification, Theory of Evolution, The Six Kingdoms
1. Define evolution: ___________________________________________________
2. For each statement below, place a check next to those that provide EVIDENCE that evolution has occurred:
___ Animals have structures they do not use (vestigial)
___ The same types of animals live in different parts of the world
___ The fossil record shows transitional species
___ Vertebrates have the same (or similar) internal structures, such as the bones of the forearm
___ Every organism has unique structures unlike any other organism
3. [ Natural / Artificial ] Selection is responsible for the many different breeds of dogs.
4. What is an adaptation? __________________________________________________________________
5. Describe how evolution would have acted on giraffes according to natural selection.
6. Who proposed the Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection? _______________________________________
7. What is the difference between a common name and a scientific name? ___________________________
8. Know the taxonomic categories used to describe how organisms are classified.
Kingdom, ___________________, Class, ____________________, Family, _______________ Species
9. What does the scientific name tell you about the organism? _____________________________________________
10. Know what types or organisms go into each of the 6 Kingdoms
Animalia ______________________________ Plantae ______________________________
Fungi ________________________________ Protista ______________________________
Archaebacteria _________________________ Eubacteria ___________________________
11. Know the difference between a(n):
prokaryote and eukaryote __________________________ unicellular and multicellular ______________________________
heterotroph and autotroph __________________________ mobile and sessile ____________________________________
12. How did Darwin’s Theory explain the different shapes and sizes among the beaks of finches on the Galapagos?
__________________________________________________________________________________________
13. According to the cladogram, which two species are most closely related? ___________________________________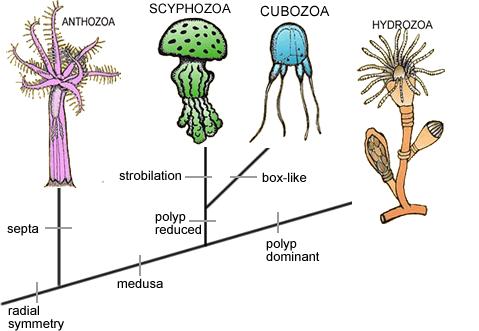
Section E: Simple Animals
9. What organisms belong to the PHYLUM PORIFERA? _________________________________________
10. Some animals are asymmetrical, what are the two types of symmetry found in other animals and provide a sketch:
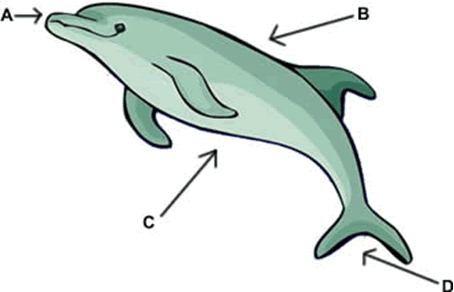
11. On the animal below, label the dorsal, ventral, posterior and anterior sides.
12. Unlike other animals, sponges do NOT have (check all that apply)
______ symmetry ______ cells ______ tissues _______ the ability to reproduce
13. Can sponges reproduce asexually? __________ Sexually? _________
14. What is a hermaphrodite? _______________________________________________________________
15. What does “sessile” mean? ____________________________________________________________
16. Name an organism that is sessile: ______________________________________________________
17. To be classified into the animal kingdom, organisms must be (check all that apply)
_____ Multicellular _____ Heterotrophic _____ Hermaphroditic ____ Mobile
18. Cnidarians use their tentacles for: ______________________________________________________
19. Which of the following forms is the medusa? Which is the polyp?
Section F: Invertebrates
Topics Covered: Roundworms, Flatworms, Mollusks, Annelids, Arthropods
1. What is regeneration? __________________________________________________________
2. Roundworms belong to the Kingdom ______________________ and the Phylum ___________________
3. How might a person contract a tapeworm? ___________________________________________________
4. Where does a parasitic tapeworm live in the body? [ blood / intestine / brain ]
5. What is the intermediate host of the schistosoma worm? _______________________________________
How would a person contract schistosomiasis? _______________________________________________
6. Flatworms, such as the planarian, belong to the Kingdom ___________________and the Phylum _______________________
7. What Phylum includes all the segmented worms, like a leech or earthworm? ______________________
8. What group of animals is characterized by an exoskeleton? ____________________________________
9. What are mandibles? ___________________________________________________________________
10. What animal has suckers, a beak, and a fin (most of you dissected it in class) ______________________
11. The digestive tract of an earthworm includes the following structures. Place them in the correct order.
___ Pharynx ___ Gizzard ____ Intestine ____ Mouth ____ Crop ____ Anus
12. In most animals, the tube that connects the mouth to the stomach is the ________________________
13. Which of those structures grinds the food? _______________________________________
Which stores food? _________________________________
Which is a muscle to help suck food (soil) in? _____________________________________
14. The arrow on the drawing points to the ________________________________
What is the function of the structure? ___________________________________
15. What are the three parts of the insect body plan? __________________________________________________
16. How many legs does an insect have? _____ How many legs does a spider have? ________
17. What is the function of the “foot” of the mollusk? ____________________________________
18. Do insects have antennae? ________ Do spiders? ____________Do crustaceans have antennae? ________________
19. What was the stiff shell-like structure you removed from the squid during the dissection? ____________
20. For each of the pairs, circle the set that is most closely related
a. crab & lobster
b. lobster & millipede
a. squid & jellyfish
b. squid & snail
a. spiders & scorpions
b. spiders & crabs
a. sea anemone & sponge
b. jellyfish & hydra
a. earthworm & leech
b. flatworm & roundworm
21. Identify the following organisms (mollusk, tapeworm, annelid, flatworm, cnidarian (hydra), crustacean)
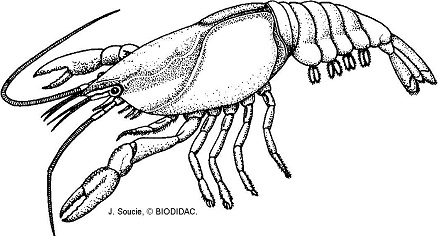
22. On the Crayfish, identify the
Antenna
Cheliped
Cephalothorax
Abdomen
Walking Legs
Swimmerets
23. Of all the phyla, which contains the largest number of species? ______________________________
24. The tentacles of a cephalopod are used for what purpose? _____________________________________
25. On the picture of the squid, identify the:
Eyes
Tentacle
Arm
Fin
Mouth
26. Check the box if it applies to the organism:
| Crustacean | Spider | Insect | |
| Has antennae | |||
| Member of Phylum Arthropoda | |||
| Has 3 body segments | |||
| Has 2 body segments, one being a cephalothorax | |||
| Has chelicerae |
27. What is metamorphosis? __________________________________________________