The Nervous System - Neurons and Neuroglial Cells
Case Story
Sarah Kate experiences paralysis and is diagnosed with multiple sclerosis.
Symptoms: Unable to focus eyes, facial paralysis, full body paralysis; link to Sarah Kate's Youtube channel
Diagnosis includes lumbar puncture and MRI, showing lesions on the brain.
The Nervous System
- includes the brain, spinal cord, and nerves
- functions to maintain coordinate body systems and maintain homeostasis
Sensory - receives information
Integrative - determines where information is sent
Motor - responds to signals
Divisions of the nervous system:
Central Nervous system - brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous system - nerves throughout the body
31 pairs of spinal nerves | 12 pairs of cranial nerves
*Damage to the spinal cord can result in paralysis
Somatic Nervous System - skeletal, voluntary
Autonomic Nervous System - smooth muscles, glands, involuntary
Parasympathetic (rest and digest) | Sympathetic (fight or flight)
*Sarah's symptoms are the result of damage to neurons
Neurons:
- masses of nerve cells that transmit information; functional unit of the nervous system
-
Cell Body: This is the central part of the neuron that contains the nucleus and other organelles
-
Dendrites: These are branch-like structures that extend from the cell body and receive incoming signals
-
Axon: Single long fibers that conduct signals away from the cell; ending in axon terminals
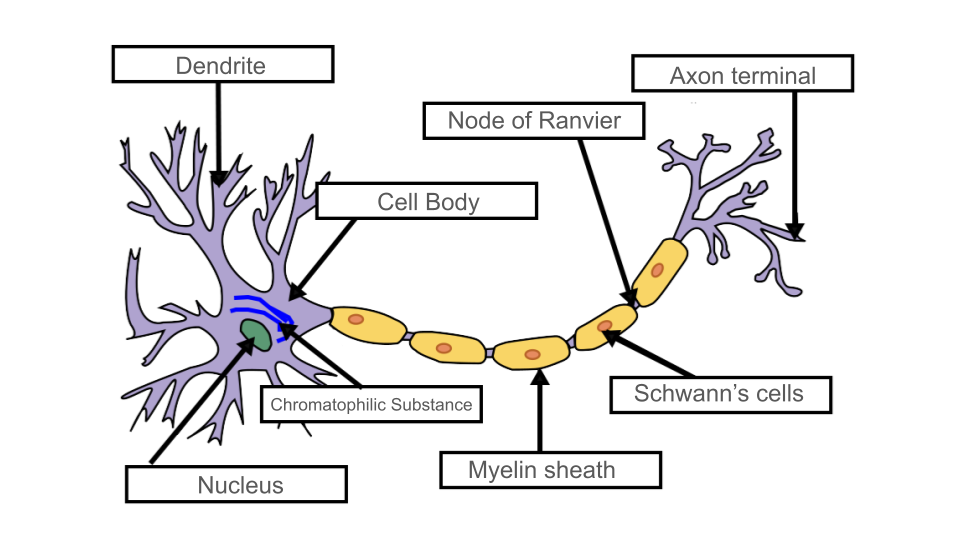
Neuroglial Cells (neuroglia)
- supportive tissue of the nervous system (more numerous than neurons). Five types
1. Microglial Cells - immune function
2. Oligodendrocytes (CNS) - produce myelin
3. Schwann cells (PNS) - produce myelin
4. Astrocytes - regulate blood flow, connect to capillaries
5. Ependymal Cells - line the ventricles of the brain and spinal cord
*Myelin Sheaths - protective covering that insulate axons
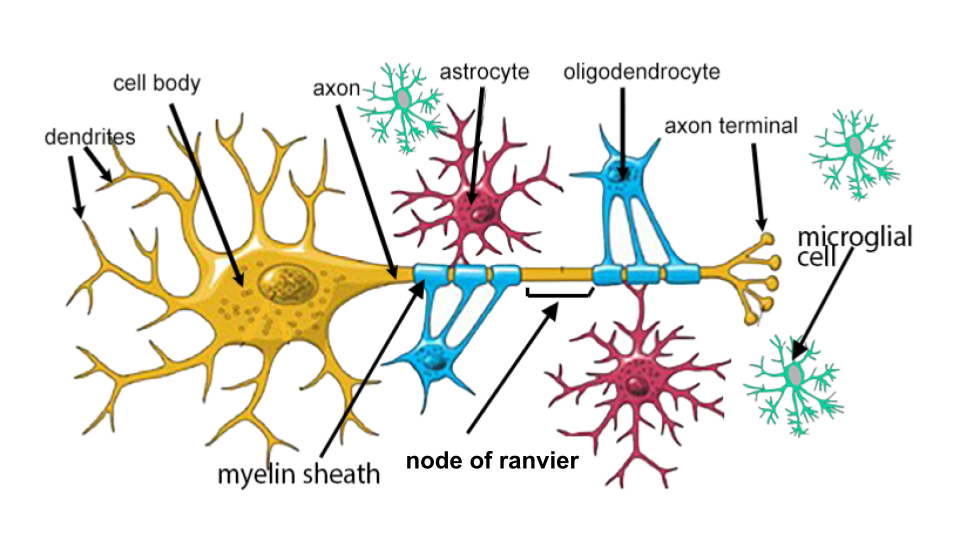
Assignment: Color the Neuron and Neuroglia
Myelin sheaths - insulate axons; damage interferes with nerve signals
In MS, demylination causes symptoms
Lesions on the brain (seen in MRS) is causes paralysis and motor symptoms
Lesions on the cerebellum can cause balance issues
MS is an autoimmune disease - immune cells attack the myelin of nerves
Sclerosis means "scarring"
Myelinated areas of the brain = white matter
Unmylinated ares of the brain = gray matter
*Graphic of MS, includes Lhermitte sign (which Sarah describes)
Nerve Impulses
Dendrites receive signal -- passes down the axon, crosses to a neighboring neuron at the synapse
Speed is proportional to the size of the axon; myelinated axons conduct impulses faster
*In MS, damaged myelin slows the speed of the impulse
Treatments for MS
- corticosteroids
- disease-modifying therapies
- muscle relaxants
-
plasma exchanges
- rehabilitation
Nerve Impulses - weak electric current; ions are sodium and potassium
The Synapse
- gap between two communicating neurons
- neurotransmitters are released at the axon terminal and cross the synapse and trigger a response on the dendrite
Types of neurotransmitters - excitatory and inhibatory
Anatomy of the synapse
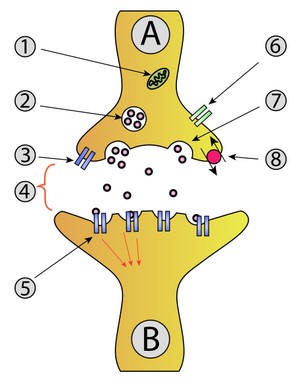
Anatomy of a Synapse: Coloring
Examples of Neurotransmitters
Acetylcholine (ACh): ACh is involved muscle contraction
Dopamine: Involved in feelings of pleasure and reinforcement and plays a crucial role in movement and coordination.
Serotonin: Serotonin regulates mood, appetite, sleep, and anxiety.
Norepinephrine (noradrenaline): Norepinephrine is involved in the body's "fight or flight" response
Endorphins: Endorphins are natural painkillers produced in response to stress or pain.
Antidepressents
SSRI - selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor; keeps serotonin active in the synapse
Drugs and the Nervous System
Cocaine - blocks reuptake of dopamine
Ecstasy (MDMA) - blocks reuptake of serotonin
Heroine - blocks release of GABA, which causes more dopamine release
Amphetamines - mimic dopamine, binds to receptors
Disorders Related to Neurons
ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis) - progressive degeneration of the nerves in the brain and spinal cord
Epilepsy - excess electrical activity causes seizures
Myasthenia Gravis - antibodies destroy neuromuscular connections (See Case Study from Muscle Unit)
Poliomyelitis - caused by a virus, causes paralysis (Polio vaccine eliminated most cases)
Alzheimer's Disease -
brain disorder that affects memory, thinking, and behavior
See Case Study on Alzheimer's Disease - Fading Memories
See also: Mini-Mental State Examination (high school edition)
Practice Labeling Images
