Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
Anatomy:
structure of body parts
Physiology:
function of body parts; what they do and how.
*Solving Crimes with the Necrobiome
 Essential Question: What happened to Kati Mori at the London Marathon?
Essential Question: What happened to Kati Mori at the London Marathon?
What were Kati's symptoms?
Homeostasis - tendency of the body to maintain a stable internal environment
Energy required to keep the body in working order
Levels of Organization
Atoms → Molecules → Macromolecules →Organelles → Cells →Tissues → Organs → Organ Systems → Organism
Characteristics (Processes) of Life
- Movement - self initiated change in __________, motion of internal parts
- Responsiveness - ability to sense changes and ______________
- Growth - increase in _________________
- Reproduction - DNA passed from parents to _________________
- Respiration - obtaining ____________________
- Digestion - chemically changing (breaking down) ______________
- Absorption -passage of digested products (food) through membranes and into ___________________________
- Circulation - movement of ________________________ throughout the body
- Assimilation -changing absorbed substances into ______________________ different substances
- Excretion - removal of ______________________
Functions / Characteristics of Human Life
1. Organization - cells, tissues, organs
2. Metabolism - reactions in the body, requires energy
3. Responsiveness - sense changes and react to them
4. Movement - change in position, motion of internal parts
5. Growth - increase in body size (also repair)
6. Reproduction - passing DNA to new individuals
7. Development - changes in the body, including differentiation.
Differentiation - the process by which cells become specialized to perform a specific function
Cells differentiate by acting and deactivating genes
Metabolism: All physical and chemical changes occurring in an organism
All of these processes require: ENERGY - Energy comes from the food we eat.
Requirements for Life
Needs: Water, food, oxygen,
heat, pressure
Article: "Why We Need Air Pressure"
Feedback Loops - how the body makes adjustments when the environment changes
Normal range indicates where the body can function, or what is optimal
Set point is the value around which the range fluctuatesSensors (receptors) - detect conditions such as temperate and relay to brain
Effectors - muscles of glands that respond. Ex. sweat glands
Negative Feedback Loop - body temperature rises, brain signals to increase sweating to return body to set point
Positive Feedback Loop - suckling by infant stimulates breast milk
Kati's Vital Signs
Vital signs are measurements of the body's basic functions (heart rate, temperature, respiration)
Vital signs indicate Kati has hyponatremia (too much water)
To treat this condition, doctors give patients a drug to increase urination
Anatomical Terminology
Anatomical position - standing upright, palms facing forward
Prone = Facedown | Supine = face up
Regional Descriptions
Superior / Inferior = above / below
Medial / Lateral = toward outside / toward inner
Anterior/ Posterior = above or toward head / below or toward tail
Proximal / Distal = closer / farther
Superficial / Deep = surface / deep
Regional Terms - each area of the body has a name | Labeling Exercise
Planes of the Body
Sagittal | Transverse | Frontal (coronal)
General Organization of the Body:
Axial Portion - head, neck, trunk | Appendicular Portion - arms & legs
VISCERA = internal organs. also: "visceral organs"
Body Cavities
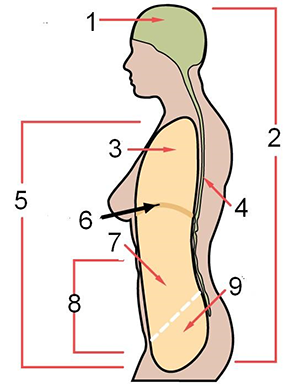
Dorsal Cavity = backside
Ventral Cavity = frontside
Cranial cavity = brain
Spinal cavity = within vertebrae, spinal cord
Thoracic = chest
Abdomen =stomach
Pelvic = lower abdoment
Abdominopelvic = abdomen + pelvic region
Diaphragm - muscle that separates thoracic from abdominal cavity
Membranes
SEROUS MEMBRANE - two layers, covers organs
outer layer = PARIETAL layer and forms a "lining"
inner layer = VISCERAL layer, covers the surface of organsPleura (or pleural membrane) - surrounds the lungs
Pericardium (or pericardial membrane) - surrounds the heart
Peritoneum (or peritoneal membrane) - surrounds organs within the abdominopelvic cavity
*Between the layers of each membrane is a lubricating fluid which is called SEROUS FLUID
*A seroma is a pocket of serous fluid (causes swelling)
Eviscerate - to remove the visceral organs
| ORGAN SYSTEMS | How does this system maintain homeostasis? | |
| 1. Integumentary | Body
covering. Skin, hair, nails, sweat glands. - protect underlying tissues, regulate body temperature |
|
| 2. Skeletal | Bones,
ligaments, cartilage - Support, movement, protection; production of blood cells |
|
| 3. Muscular | Muscles
of the body - Movement, posture, production of body heat |
|
| 4. Nervous | Brain,
spinal cord, nerves - Communication, mental activities |
|
| 5. Endocrine | Glands = pituitary, thyroid, pancreas, ovaries,
testes - Secretion of hormones, chemical communication |
|
| 6. Digestive | Mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines, - Breakdown of food (digestion), absorption |
|
| 7. Circulatory | Heart,
blood vessels, blood. - Transports materials throughout the body. |
|
| 8. Lymphatic | ( Immune System) - fights infections | |
| 8. Urinary | Kidneys,
ureters, urinary bladder, urethra - filters wastes from the blood, maintains water balance |
|
| 9. Reproductive | Reproductive
organs, primarily the ovaries (females) and testes (males) |
|
*Learn to Identify and Describe the Body Regions (Body Regions Handout)
*Learn the names of specialized medical fields. (Medical and Applied Science)