Overview of the Kingdoms of Life
Kingdom Protista
- Heterotrophic or Autotrophic
- Unicellular or Multicellular
- Mostly aquatic
- Mostly asexual
- Motile or Nonmotile
- The endosymbiosis theory explains how organisms developed organelles
Ex: Euglena, Amoeba, Paramecium, Algae, Slime Molds

Kingdom Fungi
- Heterotrophic
- Unicellular or Multicellular
- Mostly terrestrial
- Asexual or sexual
- Nonmotile
- Important decomposers in the environment
Ex: Mushrooms, molds, yeasts
Kingdom Plantae
- Multicellular
- Autotrophic
- Mostly terrestrial
- Asexual or Sexual
- Nonmotile
Ex: Trees, mosses, ferns, flowering plants
Kingdom Animalia
- Multicellular
- Heterotrophic
- Terrestrial and Aquatic
- Sexual (a few are asexual)
- Motile (a few are nonmotile)
Protostomes and deuterostomes are two major groups of animals classified based on the development of their embryonic cells and the formation of their body cavities.
-
Protostomes:
- Cleavage: During embryonic development, the first opening formed is the mouth. The cleavage (early cell divisions) in protostomes is spiral and determinate, meaning the fate of each cell is determined early in development.
- Coelom Formation: The coelom (body cavity) in protostomes typically forms from solid masses of cells that split to form a cavity. It forms from the mesoderm.
- Examples: Most invertebrates such as arthropods (insects, spiders), mollusks (snails, clams), and annelids (earthworms) are protostomes.
- Deuterostomes:
- Cleavage: In deuterostomes, the first opening formed is the anus, and the mouth develops later. Cleavage is radial and indeterminate, meaning the fate of cells isn't determined early, allowing for the development of identical twins and regeneration.
- Coelom Formation: The coelom in deuterostomes forms from an outpouching of the primitive gut. It forms from the endoderm.
- Examples: Echinoderms (starfish, sea urchins), chordates (including vertebrates like fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals) are deuterostomes.
These distinctions in embryonic development have significant implications for the body plan and development of these animals, including how their organs form and how their bodies are organized.
Protostomes - mouth develops first
Phylum Mollusca
The phylum Mollusca is a diverse group of invertebrates known for their soft bodies, often protected by a hard shell.
Class Gastropoda - snails, slugs
Class Cephalopoda - squids, octopus
Class Bivalvia - Clams, oysters
Phylum Annelida -- segmented worms
The phylum Annelida consists of segmented worms, characterized by their body segmentation and cylindrical, elongated bodies.
Polychaetes - marine predators with parapodia
Oligochaetes - terrestrial worms and leeches
Phylum Arthropoda - segmented bodies, exoskeleton, jointed appendages,
largest phyla
Subphylum Crustacea - crabs, lobsters
Subphylum Uniramia - insects
...........(Class Insecta), millipedes, centipedes
Subphylum Chelicerata - spiders, scorpions
Deuterostomes - anus develops first
Phylum Echinodermata (starfish)
** Echinoderms have radial symmetry and a unique water vascular system
for locomotion
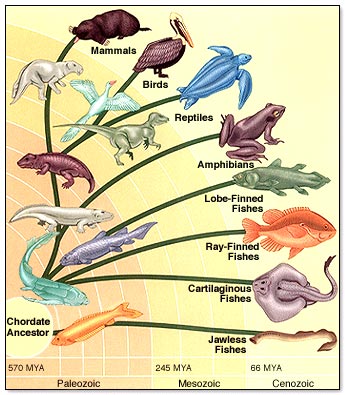
Phylum Chordata - has notochord (dorsal nerve cord)
Lanceletes & Seas Squirts are nonvertebrate chordates

Subphylum Vertebrata
In vertebrates, the notochord is replaced by the vertebral column. Most vertebrates also have a head region, endoskeleton, and paired appendages.
1. Jawless Fishes (lamprey & hagfish)
2. Cartilage Fishes (sharks & rays)
3. Bony Fishes (salmon, goldfish, carp)
4. Amphibians
5. Reptiles
6. Birds
7. Mammals