Chromosomal Inheritance
Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance:
-
Chromosomes contain genetic information: The theory proposes that chromosomes, found in the nucleus of cells, carry the genetic information in the form of genes. Genes are specific segments of DNA that encode instructions for building proteins or RNA molecules, which ultimately determine an organism's traits.
-
Chromosomes come in pairs: In sexually reproducing organisms, chromosomes are inherited in pairs, with one set originating from each parent. These pairs of chromosomes, known as homologous chromosomes, carry similar genes, although they might have different versions (alleles) of those genes.
-
Segregation and independent assortment: During the formation of gametes (sperm and egg cells), chromosomes undergo segregation and independent assortment. This occurs through the process of meiosis, where homologous chromosomes separate, leading to the random distribution of alleles into gametes. This process allows for genetic variation as different combinations of alleles can be passed on to offspring.
-
Mendelian principles and chromosomes: The Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance reconciles the principles of inheritance proposed by Gregor Mendel with the behavior of chromosomes. Mendel's laws of segregation and independent assortment of alleles align with the way chromosomes segregate and assort during meiosis.
-
Linkage and recombination: The theory also explains the concepts of linkage and recombination. Genes located on the same chromosome tend to be inherited together (linkage), but crossing over during meiosis can result in the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes, leading to genetic recombination and the creation of new combinations of alleles.
The Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance provided a framework for understanding how the transmission of genetic traits occurs and how the behavior of chromosomes during cell division (particularly during meiosis) is linked to the inheritance patterns observed in offspring. This theory laid the groundwork for modern genetics and the understanding of how genes are located on chromosomes and transmitted from one generation to the next.
Human karyotype
Sex Linked Genes
Genes located on the X chromosome are inherited with that X. When doing crosses you must include the sex chromosomes in your cross. Use superscript letters for the allele.
Human X-Linked Disorders
Colorblindness –
Muscular Dystrophy -
Hemophilia -
Fragile X Syndrome -
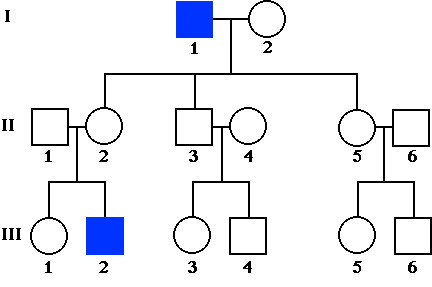
Pedigree Studies
Human traits are tracked by creating a chart showing how a trait is passed from one generation to the next
This one shows a sex linked trait. Can you find the carriers?